Over the past couple of months, we have seen major changes within the Google shopping experience. We first noticed these changes from last year’s announcement around Search On and we’re still seeing significant impacts within the organic space today.
We talked about most of these changes in our last article on organic ecommerce, which we highly recommend you check out if you have not, because it touches on how these new experiences impact your organic presence. This time around, we’re going to explain how Google’s shift to those richer experiences has increased our dependency on Google Merchant Center (GMC) and how beneficial GMC can be for both SEOs and teams managing large feeds.
-
It unlocks free shopping listings 🛒
The first reason why GMC is hyper-relevant to SEO for ecommerce brands is that it enables you to show up for free listings within the Google shopping experience. We do not yet know how this impacts other traditional ranking factors, but it is important to note that free listing URLs are those from feeds. We have seen brands tagging these URLs and those are the URLs coming through when we select them from free listings.
We highly recommend you tag these URLs to easily identify high-trafficked free listings as GMC can be very limited in analysing this organic data. Additionally, since the increased presence of free listings we have seen a large amount of product page data being under reported in Google Search Console (GSC).
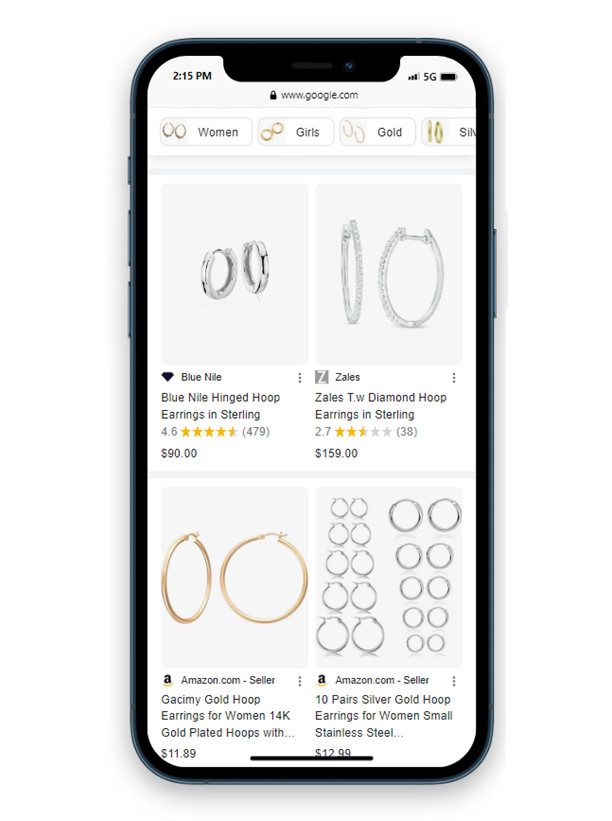
Google Search Console also just rolled out a “merchant listings” report that can help you better optimise your free listings, which could be super helpful for feed managers.
-
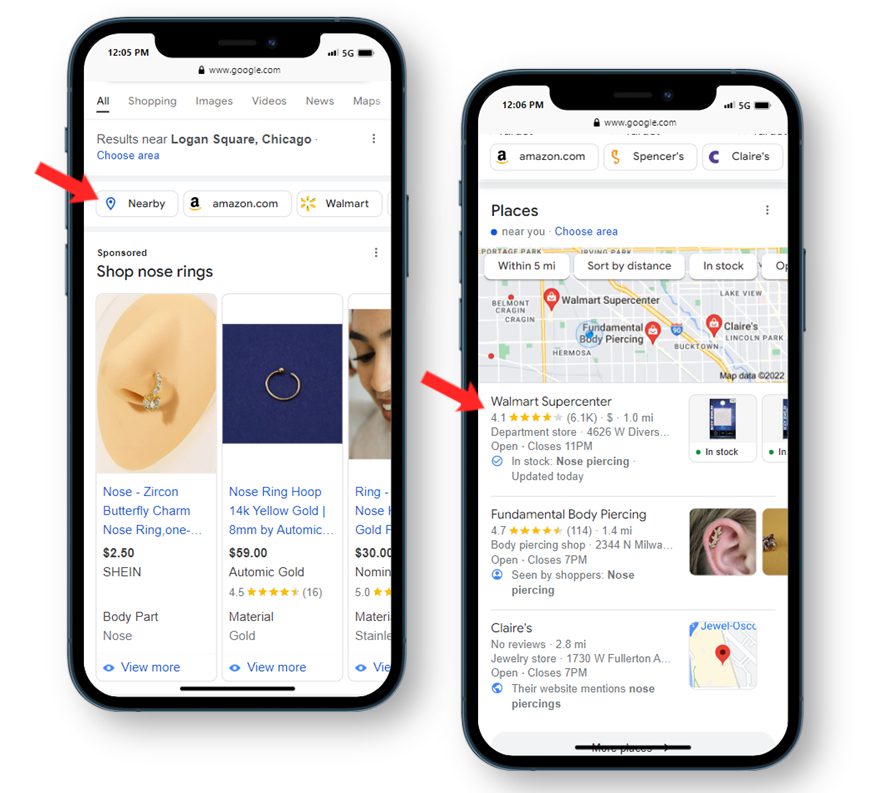
Your local visibility will improve 📍
Google officially updated terms within their Business Profile Help Center to state that adding in-store products can improve local visibility. This is managed through Google Merchant Center with local feeds.
Additionally, we have seen the “nearby” filtered carousel pop up on more top-of-funnel search terms, as well as a direct correlation of non-brand terms without “near me” qualifiers driving local page traffic in Google Search Console.
-
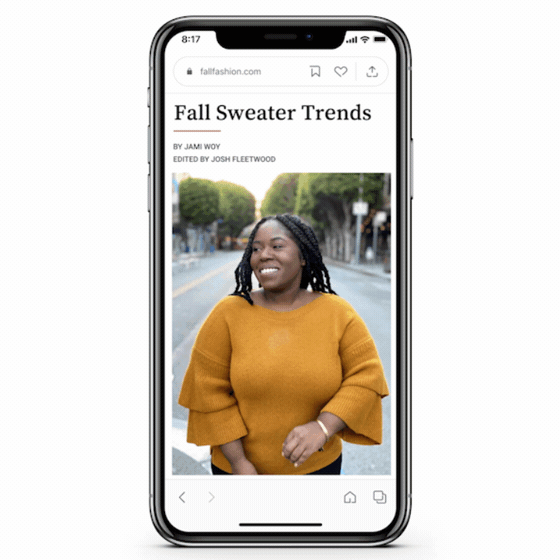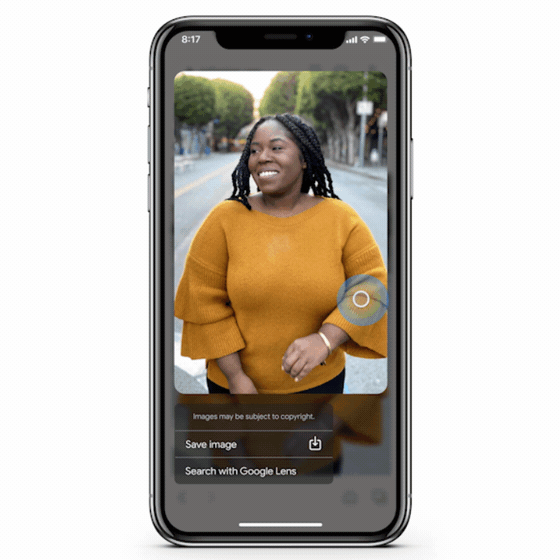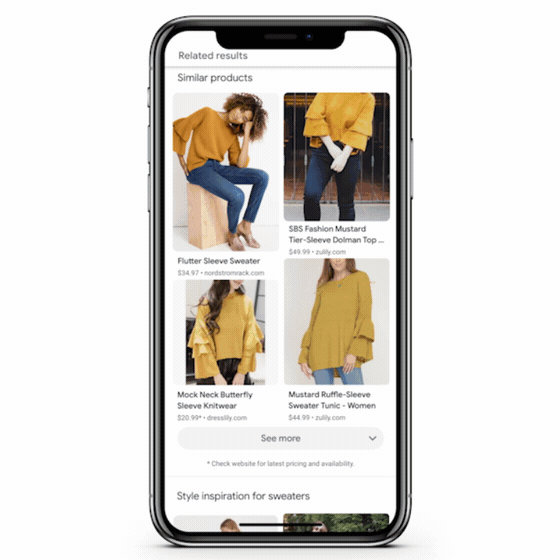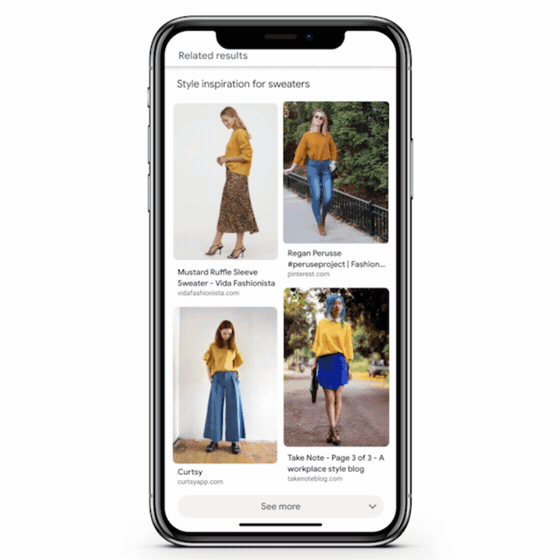
You’ll be more likely to appear in Google Lens 📱
Over the years, Google has made huge strides in connecting the physical and digital worlds with its search engine. None have been more exciting than the evolution of Google Lens. This image-recognition technology allows users to upload photos to search and shop products, translate languages, and identify landmarks in real time.
GIF: Google
Google Lens presence is made possible through GMC, structured data, and/or image optimisation. By adding additional context about products details in free listings as well as aligning to Google’s image optimisation best practices, you can improve your chances of showing up within the Google Lens experience.
-
Schema and GMC work together 🤝
In the ecommerce space, site needs can very brand to brand. When and how often your product content is updated can dictate your presence on Google across the various search experiences.
Leveraging Google Merchant Center and coordinating with your feed manager will prevent data inconsistencies. Additionally, Google does not guarantee how long it takes before changes on your site will be processed through crawling. Feeds can be used on a weekly, daily, or even hourly cadence based on your brand’s needs to keep this information up to date.
Experience Structured Data Google Merchant Center Product rich results in Google Search Google Search uses Product structured data to display product rich results. Google Search may use Google Merchant Center data to display product rich results. Google Images results with product annotations Google Images uses Product structured data to display product annotations on images. Google Images uses images listed in Google Merchant Center. Google Shopping tab Adding structured data can help Google Merchant Center in some cases (for example, during data verification). Participation in Google Merchant Center is required to appear in the Google Shopping tab. Google Lens image search results Google Lens uses image structured data properties where available. Google Images uses images listed in Google Merchant Center. Additionally, Content API in feeds allows for immediate content updates, which can help share information that is not present on your website, like local specific pricing or inventory.
-
It’ll supercharge your indexing 🗄️
Last but not least, Google Merchant Center feeds can help with your SEO internal linking and indexing strategies. Google strongly recommends linking to all pages, but in the event that large ecommerce sites cannot, the search giant recommends using sitemaps and Google Merchant Center feeds. This gives webmasters another way to specify which products should be indexed. It’s a feature that is just not talked about enough within the SEO community.
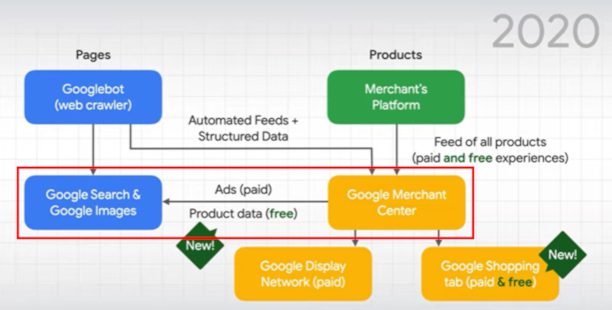
Image: Google Search Central
In conclusion, Google has made some major moves that should increase our dependency on Google Merchant Center. Although this is not a traditional tool or skill set leverage by most SEOs, it would be in your best interests to learn the ins and outs of GMC sooner rather than later.
Need a little help? Partner with us to take your ecommerce tactics to the next level—now and in the future. Let’s talk!




